Access Control Making Your Life Secure and Easy

Access Control Definition
Access control is a security process that regulates who or what can view or use resources in a computing background. It is a basic concept in security that minimizes risk to the business or community.
Access Control Types
There are two types: physical and logical. Physical access control limits access to campuses, structures, spaces, and physical IT assets. Logical access control limits links to computer networks, system files, and data.
The major models of access control are the following:
Mandatory access control (MAC):
This is a security model in which access rights are regulated by a central authority based on multiple tiers of security. Often used in government and military backgrounds, classifications are assigned to system resources and the operating system (OS) or security kernel. It grants or denies access to those resource entities based on the information security clearance of the user or device. For example, Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a part of MAC on the Linux OS.
Discretionary access control (DAC):
This is an method in which owners or administrators of the protected system, data, or resource set the policies defining who or what is allowed to access the resource. Many of these systems allow administrators to limit the propagation of access rights. A common complaint of DAC systems is a lack of centralized control.
Role-based access control (RBAC):
This is a widely used mechanism that restricts access to computer resources based on individuals or companies with defined business functions example, executive level, engineer level 1, etc. rather than the self-identity of individual users. The role-based security model depends on a complex structure of role assignments, role authorizations, and role licenses developed using role engineering to regulate employee access to systems. RBAC systems can be used to enforce MAC and DAC frameworks.
Rule-based access control:
This is a security model in which the system administrator defines the rules that control access to resource objects. Often, these rules are based on circumstances, such as time of day or location. It is not unusual to use some form of both rule-based access control and RBAC to enforce access policies and processes.
Attribute-based access control (ABAC):
This is a methodology that manages access privileges by evaluating a set of rules, policies, and relationships using the details of users, systems, and environmental conditions.
Access control in information security
Access control systems are complex and can be questioning to manage in dynamic IT environments that involve on-premises systems and cloud services. After some high-profile breaches, technology vendors have shifted away from single sign-on (SSO) systems to unified access management, which offers access controls for on-premises and cloud surroundings.
This systems perform identification authentication and authorization of users and entities by considering required login credentials that can include passwords, personal label numbers (PINs), biometric scans, security tokens, or other authentication aspects. Multifactor authentication (MFA), which requires two or more authentication factors, is often an important part of layered security to protect access control systems.

Access control Network Security
An access control network is the act of keeping unauthorized users and devices out of a personal network. Organizations that give certain devices or users from out of the organization occasional access to the network can use network access control to guarantee that these devices meet corporate security compliance rules.
The increasingly authorized use of non-corporate devices accessing corporate networks requires businesses to pay special attention to network security, including who or what is permitted access. Network security protects the functionality of the network, guaranteeing that only authorized users and devices have access to it, that those devices are clean, and that the users are who they say they are.
ACN, is one part of network security. There are many ACN tools available, and the functions are often performed by a network access server. Effective network access control limits access to only those devices that are authorized and compliant with security policies, meaning they have all the required security patches and anti-intrusion software. Network operators specify the security policies that decide which devices or applications yield with endpoint security requirements and will be allowed network access.

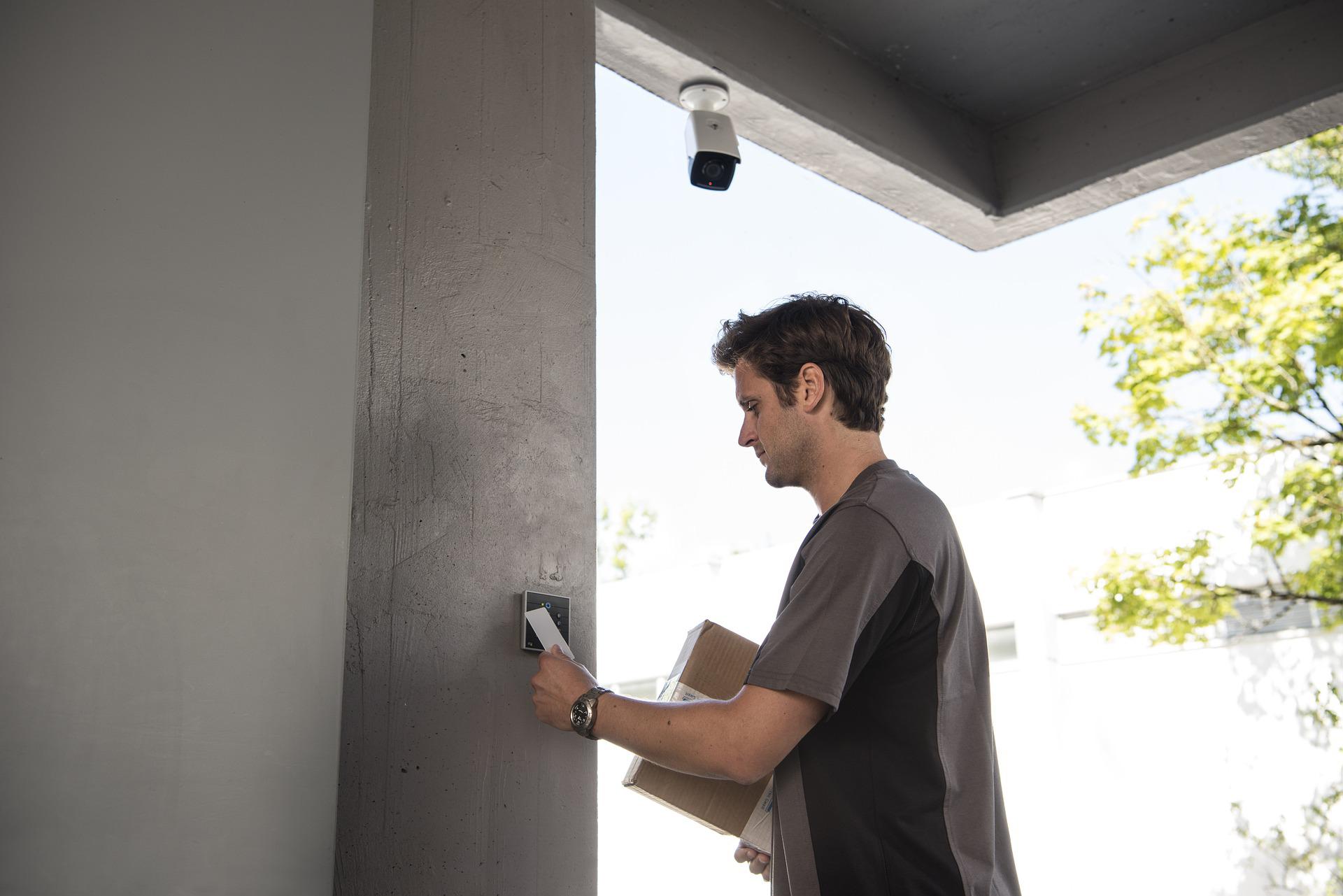
RFID system in Access control
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track various objects. Most RFID systems have a microchip with an antenna (tag), a reader with an antenna and an access control server.
An RFID system cross-references the data reserved on the tag with its own database. If it matches the data, the access is then allowed.
RFID Frequencies
Frequency is the length of the radio waves utilized to communicate between system elements. RFID technology includes various frequency levels that determine the solution's reading range. The more down the frequency, the shorter the reader's range.
Common frequency ranges:
Low Frequency 120 - 150 kHz (LF)
High Frequency 13.56 MHz and higher (HF)
Ultra-High Frequency 860 - 980 MHz (UHF)
Microwave Frequency 2.45 GHz and higher
Understanding the frequencies at which RFID systems work will help you to choose the correct solution for your application. Radio waves work differently at each of these frequencies and there are pros and cons associated with using each frequency band.
An RFID system with a lower frequency can read better near liquid or metal surfaces, however, it has a slower data read rate. Higher frequency systems have faster data transfer rates and longer read ranges but are more exposed to radio wave interference caused by liquids and metals in the circumstances.
That being said, technology advancements in recent years have made it possible to utilize ultra-high frequency RFID around liquids and metals.
RFID Tags
RFID tags consist of three essential elements: a microchip, antenna and a substrate. The microchip within the tag is what stocks and processes information, modulates and demodulates radio-frequency signals. And antenna enables the tag to receive and transmit the signal.
RFID tags can be differentiated by their power supply. There are two main types of tags utilized in the industry - passive and active tags.

What is fingerprint access control?
With fingerprint access control, you use a fingerprint scanner to create a template for each person you like to authorise for access. Then when they show their finger at a fingerprint reader, for example by a door, it's compared with the kept template in your database. If it's a match, they're given access.
Key benefits
Security, comfort and affordability are the three main reasons why so many organisations are opting for fingerprint-based access control. Here, we look at each use in more additional detail.

Increased security
Inherent identification:
As a fingerprint is part of the body, gaining entry with one that's not your own is far more complicated than stealing an access card.
Difficult to duplicate:
Traditional access cards and fobs can effortlessly be replicated, which makes legacy access control systems very weak. A fingerprint is much harder to copy. And most modern biometric systems use liveness tests that measure aspects such as blood flow to ensure the fingerprint's from a living person.
Verification:
Fingerprint testing can count an extra layer of security to your access control either at every access point or just at higher security areas. The person trying to gain access is first identified by their access card. Then they present their fingerprint to confirm they're the cardholder.
Online management:
Each person's data is stored digitally using fingerprint access control software. So, with a software-based access control system like AEOS, organizing and revoking permissions is easy and fast.

Convenience
Can't be forgotten or lost:
It's so easy to forget a password or code, specifically as we have so many to remember today. And forgetting or misplacing an access card is just as easy to do. With fingerprint access, you always have your identifier with you.
No fumbling:
In many situations, especially those where speed is important or people are bringing other items, pulling out and using an access card can be very inappropriate or impractical.
Fast and efficient:
Most fingerprint readers can recognize people in less than a second. Which is much faster than using a password or PIN or keeping a manual ID check.
Mass market knowledge:
Fingerprint identification is now used in a variety of settings, with many people using it on their smartphone, for example. As most people are aware with it, there's little need for training on its use.
Cost management
Lower price point:
Fingerprint identification is one of the most cheap options for biometric access control. Which makes it a cost-effective for a wide variety of applications.
No identifiers to buy:
The cost of publishing and replacing access control cards, badges or fobs can add up to a staggering amount. Particularly for large societies. With fingerprint access control, there's no identifier to purchase, and you don't need to pay for replacements or the administration involved in replacements.
Lower staffing costs:
The increased security offered by fingerprint access control often means you can decrease the number of security staff at your access points.
Protect your assets:
One of the key purposes for access control is, of course, to prevent unauthorized people acquiring access to your physical assets and data. Investing in a fingerprint access control system helps you to bypass the many and varied costs that can occur when someone manages to gain access without permission.

Access control policy
To secure a facility, organizations use electronic access control systems that depend on user credentials, access card readers, auditing, and reports to follow employee access to restricted business areas and proprietary areas, such as data centers. Some of these systems contain access control panels to restrict entry to rooms and buildings, as well as warnings and lockdown capabilities, to prevent unauthorized access.
Access control system Pakistan
The goal of access control in Pakistan is to minimize the security risk of unauthorized access to physical and logical systems. Access control is a essential component of security in Pakistan which compliance programs that ensures security technology and access control policies are in place to guard confidential information, such as customer data. Most organizations in Pakistan have infrastructure and procedures that restrict access to networks, computer systems, applications, files and sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII) and intelligent property.